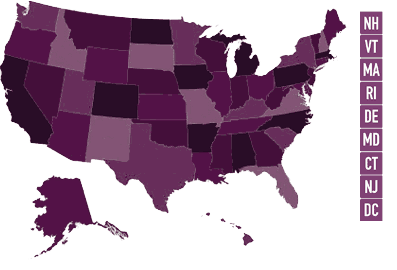
States that Allow CNMs to Practice and Prescribe Independently vs those that Require a Collaborative Agreement
Although certified nurse-midwives (CNM) hold national certification and state licensure to practice in all 50 states, including the District of Columbia, their scope of practice is often slightly different, depending on whether they have authority to practice independently or through a collaborative practice agreement with a physician. While some states allow CNMs and other advanced practice registered nurses to practice with full autonomy, other states require some level of physician oversight or otherwise require them to enter into a collaborative agreement with a physician.
Depending on the states, CNMs may practice:
- Not Independently: 19 states require CNMs to enter into a written agreement with a collaborating physician that specifies exactly what actions, interventions or therapies require the general or direct supervision of a physician.
- Independently, but with an Rx Collaborative Agreement: 7 states allow CNMs to practice independently, but without prescriptive authority. CNMs in these states interested in gaining prescriptive authority must enter into a collaborative agreement to lawfully prescribe pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic therapies.
- Independently: 25 states do not require a written collaborative agreement, supervision, or any other conditions for practice or prescriptive authority. These states respect the full autonomy of CNMs and other advanced practice RNs.
What’s the Issue with Collaborative Agreements?
Collaboration among healthcare providers has always been encouraged. However, the need for signed collaborative agreements between physicians and advanced practice registered nurses (including certified nurse-midwives) has been passionately debated in recent years. Key industry stakeholders including the American College of Nurse-Midwives (ACNM) and the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSB), oppose the signed collaborative agreement as a condition for licensure, reimbursement, hospital credentialing, clinical privileging, or prescriptive authority and believe CNMs should be able to practice to the full extent of their education and training.
The Standards for the Practice of Midwifery clearly state that midwifery care is based upon written practice guidelines that include consultation, collaboration, and referral but do not require signed collaborative agreements with physicians.
According to the ACNM, states without signed collaborative practice agreements better facilitate effective relationships between healthcare professionals, thereby allowing nurse-midwives and physicians to collaborate while still providing quality care that falls within their respective scopes of practice.
Choose A State To View CNM Regulations
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
States That Currently Require CNMs to Have a Collaborative Practice Agreement in Place with a Physician
Alabama
Alabama Board of Medical Examiners: The Legislature of the State of Alabama declares that the recognition and regulation of all areas of advanced practice nursing and the collaborative practices between licensed physicians and certified registered nurse practitioners and certified nurse midwives are essential to protect and maintain the public health and safety.
Arkansas
Arkansas State Board of Nursing: To qualify as a certified nurse midwife, an applicant must:
(A) Hold current certification as a nurse midwife from the American College of Nurse Midwives or other nationally recognized certifying body; and (B) Have an agreement with a consulting physician if providing intrapartum care.
California
California Board of Registered Nursing: The Legislature granted the CNM an independent scope of practice. CNMs practice in collaboration and consultation with physicians. The degree of collaboration in this team approach depends upon the medical needs of the individual woman or infant and the practice setting. All complications shall be referred to a physician immediately and the CNM provides emergency care until physician assistance can be obtained. By law, California nurse-midwifery care requires the supervision of a licensed physician and surgeon, but supervision does not require physical presence of the physician.
Florida
Florida Board of Nursing: In Florida, an Advanced Registered Nurse Practitioner (ARNP) is defined as “any person licensed in this state to practice professional nursing and certified in advanced or specialized nursing practice, including certified registered nurse anesthetists, certified nurse midwives, and nurse practitioners.” An Advanced Registered Nurse Practitioner shall only perform medical acts of diagnosis, treatment, and operation pursuant to a protocol between the ARNP and a Florida-licensed medical doctor, osteopathic physician, or dentist.
Learn more about becoming a nurse midwife in Florida on our Florida state page.
Delaware
Delaware Board of Nursing: All new APRN graduates and those nurses seeking to obtain independent practice must practice under a collaborative agreement for 2 years and a minimum of 4,000 full-time hours.
Georgia
Georgia Board of Nursing: An advanced practice registered professional nurse who uses a protocol must adhere to a written nurse protocol which is a written document mutually agreed upon and signed by the nurse and licensed physician which specifies delegated medical acts delegated by the physician to the nurse and provides for immediate consultation with the delegating physician or a physician designated in the absence of the delegating physician.
Learn how to become a midwife in Georgia on our Georgia state page.
Illinois
Illinois Board of Nursing: A written collaborative agreement is required for all advanced practice nurses engaged in clinical practice, except for advanced practice nurses who are authorized to practice in a hospital, hospital affiliate, or ambulatory surgical treatment center.
Kansas
Kansas State Board Nursing: Authorization for collaborative practice shall mean that an APRN is authorized to develop and manage the medical plan of care for patients or clients based upon an agreement developed jointly and signed by the APRN and one or more physicians. Each APRN and physician shall jointly review the authorization for collaborative practice annually.
Louisiana
Louisiana State Board of Nursing: Collaborative practice agreement means a formal written statement addressing the parameters of the collaborative practice which are mutually agreed upon by the advanced practice registered nurse and one or more licensed physicians or dentists which shall include but not be limited to the following provisions: (a) Availability of the collaborating physician or dentist for consultation or referral, or both. (b) Methods of management of the collaborative practice, which shall include clinical practice guidelines. (c) Coverage of the health care needs of a patient during any absence of the advanced practice registered nurse, physician, or dentist.
Mississippi
Mississippi Board of Nursing: An advanced practice registered nurse shall perform those functions authorized in this section within a collaborative/consultative relationship with a dentist or physician with an unrestricted license to practice dentistry or medicine in this state and within an established protocol or practice guidelines, as appropriate, that is filed with the board upon license application, license renewal, after entering into a new collaborative/consultative relationship or making changes to the protocol or practice guidelines or practice site.
Missouri
Missouri Board of Nursing: In order to perform advanced practice registered nurse delegated medical acts that would be specified in a written collaborative practice arrangement with a physician, meeting the requirements of the Advanced Practice Registered Nurse Rule and, thereby, securing a ‘Document of Recognition’ is a necessary precursor. Grounds exist for investigation and discipline of registered professional nurses’ and physicians’ licenses for engaging in written collaborative practice arrangements wherein the delegations are to the registered professional nurse as an advanced practice registered nurse when the particular nurse is not recognized as an advanced practice registered nurse within any clinical nursing specialty area or role.
Nebraska
Nebraska Health and Human Services: CNMs are authorized, under the provisions of a written practice agreement with a collaborating licensed practitioner, to provide delegated medical acts including managing care during pregnancy, labor, delivery, and after-birth phases for both the mother and newborn. CNMs may also provide gynecological and women’s health service at times other than pregnancy. The collaborating licensed practitioner(s) shall be responsible for supervision through ready availability for consultation and direction to the CNM when any delegated medical functions are provided.
North Carolina
North Carolina Board of Nursing: A person may practice midwifery in a hospital or non-hospital setting and shall practice under the supervision of a physician licensed to practice medicine who is actively engaged in the practice of obstetrics.
Check out steps for how to become a midwife in NC.
Ohio
Ohio Board of Nursing: A certified nurse-midwife, certified nurse practitioner, or clinical nurse specialist engaged in the practice of the nurse’s specialty, shall enter into a written standard care arrangement with one or more collaborating physicians or podiatrists whose practice is the same or similar to the nurse’s practice. A clinical nurse specialist without a certificate to prescribe whose nursing specialty is mental health or psychiatric mental health is not required to enter into a standard care arrangement.
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania State Board of Nursing: A nurse-midwife may not engage in midwifery practice without having entered into a collaborative agreement and having filed the collaborative agreement with the Board, and shall only engage in midwifery practice in accordance with the midwife practice guidelines and collaborative agreements. A collaborative agreement must contain either an acknowledgement that the nurse-midwife shall practice under the midwife practice guidelines, or that the nurse-midwife shall practice under the midwife practice guidelines as expanded or modified in the collaborative agreement.
If you’re interested in learning how to become a midwife in PA, take a peek at our Pennsylvania page.
South Carolina
South Carolina Board of Nursing: A licensed nurse practitioner, certified nurse-midwife, or clinical nurse specialist must provide evidence of approved written protocols, as provided in this section. A licensed NP, CNM, or CNS performing delegated medical acts must do so under the general supervision of a licensed physician or dentist who must be readily available for consultation
South Dakota
South Dakota State Board of Nursing: A collaborative agreement defines or describes the agreed upon overlapping scope of advanced practice nursing and medical functions that may be performed. A copy of each collaborative agreement shall be maintained on file with and be approved by the boards.
Virginia
Virginia Board of Nursing: A nurse practitioner licensed in a category other than certified registered nurse anesthetist shall be authorized to render care in collaboration and consultation with a licensed patient care team physician as part of a patient care team.
To learn how to become a midwife in VA visit our Virginia state page for more information.
Wisconsin
Wisconsin Board of Nursing: No person may engage in the practice of nurse-midwifery unless each of the following conditions is satisfied: 441.15(2)(a). The person is issued a license by the board ; and 441.15(2)(b). The practice occurs in a health care facility approved by the board, in collaboration with a physician with postgraduate training in obstetrics, and pursuant to a written agreement with that physician.
States that Require a Written Collaborative Agreement Only for Prescriptive Authority
Indiana
Indiana State Board of Nursing: An advanced practice nurse may be authorized to prescribe legend drugs, including controlled substances, if the advanced practice nurse enters into a written collaborative practice agreement. The written collaborative practice agreement sets forth the manner in which the Advanced Practice Nurse and Licensed Practitioner will cooperate, coordinate, and consult with each other in the provision of health care to patients.
Kentucky
Kentucky Board of Nursing: According to Kentucky law, Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRNs) have been authorized to prescribe non-scheduled legend drugs and controlled substances to their patients/clients after acquiring a written collaborative agreement with a physician licensed in Kentucky. Before an APRN engages in prescribing or dispensing non-scheduled legend drugs, the APRN must enter into a written collaborative agreement for prescriptive authority for non-scheduled drugs (CAPA-NS).
Before the APRN is authorized to prescribe controlled substances to their patients/clients they must acquire a collaborative agreement (CAPA-CS) with a physician licensed in Kentucky in the same or similar practice.
Michigan
Michigan Department of Licensing and Regulatory Affairs: Licensed nurse specialists are prohibited from independently prescribing controlled substances in Michigan. A licensed nurse anesthetist cannot prescribe controlled substances in any circumstance. Under the delegation of a supervising licensed physician, a licensed nurse practitioner or nurse midwife may prescribe controlled substances in Schedules 3-5. The prescription of Schedule 2 controlled substances can be delegated if the physician and the nurse practitioner or nurse midwife are both practicing within a hospital, surgical outpatient facility, or hospice.
Oklahoma
Oklahoma Board of Nursing: The Oklahoma Nursing Practice Act requires current licensure as a Registered Nurse and as an Advanced Practice Registered Nurse with prescriptive authority recognition from the Oklahoma Board of Nursing prior to prescribing or ordering drugs or medical supplies or identifying oneself as an Advanced Practice Registered Nurse with prescriptive authority recognition.
Tennessee
Tennessee Board of Nursing: Certification by the Tennessee Board of Nursing to prescribe and/or issue legend drugs shall authorize a nurse practitioner to prescribe and/or issue such drugs. Any nurse who prescribes and/or issues drugs without proper certification by the Tennessee Board of Nursing shall be subject to disciplinary action by the Board of Nursing.
Texas
Texas Board of Nursing: When applying for Prescriptive Authority in an advanced practice role and specialty, applicants must have current, valid full or provisional authorization to practice in that role and specialty in the State of Texas. Check out our Texas state page to learn more about becoming a midwife in Texas.
West Virginia
West Virginia Board of Examiners for Registered Professional Nurses: The board shall, in its discretion, authorize a nurse-midwife to prescribe prescription drugs in a collaborative relationship with a physician licensed to practice in West Virginia and in accordance with applicable state and federal laws. An authorized nurse-midwife may write or sign prescriptions or transmit prescriptions verbally or by other means of communication.
States in which CNMs have Full Prescriptive Authority and the Ability to Practice Independently
Alaska
Alaska Board of Nursing: The Alaska Board of Nursing, through its regulations, recognizes the scope of practice statements of national certification bodies recognized by the Board. CNM scope of practice in Alaska is therefore defined by the American College of Nurse-Midwives’ (ACNM)
Arizona
Arizona State Board of Nursing: CNMs are noted to have an expanded scope of practice within a specialty area that includes making independent decisions in solving complex client care problems. diagnosing, performing diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, and prescribing, administering and dispensing therapeutic measures, including legend drugs, medical devices and controlled substances within the scope of registered nurse practitioner practice on meeting the requirements established by the board.
Check out our Arizona state page to learn how to become a midwife in Arizona.
Colorado
Colorado Board of Nursing: An advanced practice nurse shall practice in accordance with the standards of the appropriate national professional nursing organization and have a safe mechanism for consultation for collaboration with a physician or, when appropriate, referral to a physician. Advanced practice nursing also include, when appropriate, referral to other healthcare providers.
Connecticut
Connecticut State Department of Public Health: Nurse-midwives shall practice within a health care system and have clinical relationships with obstetrician-gynecologists that provide for consultation, collaborative management or referral, as indicated by the health status of the patient. Nurse midwifery care shall be consistent with the standards of care established by the American College of Nurse-Midwives.
Hawaii
Hawaii Board of Nursing: The scope of an advanced practice registered nurse includes but is not limited to advanced assessment and the diagnosis, prescription, selection, and administration of therapeutic measures including over the counter drugs, legend drugs, and controlled substances within the advanced practice registered nurse’s role and specialty-appropriate education and certification.
Idaho
Idaho Board of Nursing: The advanced practice registered nurse is a licensed independent practitioner who shall practice consistent with the definition of advanced practice registered nursing, recognized national standards and the standards set forth in these rules.
Iowa
Iowa Board of Nursing: The ARNP practices within their scope of practice based upon their educational background and the standards and guidelines established by their national certifying body (i.e. American Nurses Credentialing Center, American Academy of Nurse Practitioners). In Iowa, an ARNP may practice independently. However, an ARNP may have a collaborative agreement with a physician or physicians if their practice so warrants, but this agreement is not a requirement of the Iowa Board of Nursing.
Maine
Maine State Board of Nursing: The certified nurse-midwife provides only those health care services for which the certified nurse-midwife is educationally and clinically prepared and for which competency has been maintained.
Maryland
Maryland Board of Nursing: A certified nurse midwife may perform the following functions: (1) Independent management of clients appropriate to the skill and educational preparation of the certified nurse midwife and the nurse midwife’s clinical practice guidelines; (2) Consult or collaborate with a physician or other health care provider as needed; and (3) Refer clients with complications beyond the scope of practice of the certified nurse midwife to a licensed physician.
Massachusetts
Massachusetts Board of Registration in Nursing: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) means a currently licensed Massachusetts Registered Nurse (RN) who has current authorization by the Board to engage in advanced practice nursing activities. APRN practice activities include, but are not limited to: advanced assessment; diagnosis; treatment, referrals, consultations, and other modalities for individuals, groups or communities across the life span for health promotion or health maintenance and for those who are experiencing acute or chronic disease, illness, trauma or other life-altering event in which rehabilitative, and/or palliative interventions are necessary. APRN practice is defined to include only those activities within the APRN’s authorized clinical category, scope of practice competencies, and accepted standards of Advanced Practice Nursing.
If midwifery school in Massachusetts sounds like a good fit, visit our Massachusetts state page to find more information.
Minnesota
Minnesota Board of Nursing: CNM and CRNA are not required to have a collaborative management agreement nor a written prescribing agreement (except for a CRNA who will provide nonsurgical therapies for acute or chronic pain – see below). CNPs and CNSs beginning practice after July 1, 2014, must practice for at least 2,080 hours within the context of a collaborative management setting in a hospital or integrated clinical setting where APRNs and physicians work together. A written prescribing agreement is not required.
Montana
Montana Board of Nursing: A person licensed under this chapter who holds a certificate in a field of advanced practice registered nursing may practice in the specified field of advanced practice registered nursing upon approval by the board of an amendment to the person’s license granting a certificate in a field of advanced practice registered nursing. The board shall grant a certificate in a field of advanced practice registered nursing to a person who submits written verification of certification by a board-approved national certifying body appropriate to the specific field of advanced practice registered nursing and who meets any other qualification requirements that the board prescribes.
Nevada
Nevada Board of Nursing: An advanced practice registered nurse may perform the following acts in addition to the functions of a registered nurse if the advanced practice registered nurse is properly prepared and the acts are currently within the standard of practice for his or her role and population of focus:
- Systematically assess the health status of persons and families by: (a) Taking, recording and interpreting medical histories and performing physical examinations; and (b) Performing or initiating selected diagnostic procedures.
- Based on information obtained in the assessment of a person’s health, manage the care of selected persons and families with common, acute, recurrent or long-term health problems. Management may include: (a) Initiation of a program of treatment; (b) Evaluation of responses to health problems and programs of treatment; (c) Informing a person or family of the status of the patient’s health and alternatives for care; (d) Evaluation of compliance with a program of treatment agreed upon by the person or family and the advanced practice registered nurse; (e) Modification of programs of treatment based on the response of the person or family to treatment; (f) Referral to appropriate providers of health care; and (g) Commencement of care required to stabilize a patient’s condition in an emergency.
New Hampshire
New Hampshire Board of Nursing: CNMs are regulated as a category of advanced practice registered nurse (APRN). APRN scope of practice specifically includes “performing acts of advanced assessment, diagnosing, prescribing, selecting, administering, and providing therapeutic measures and treatment regimens; obtaining consultation, planning, and implementing collaborative management, referral, or transferring the care of the client as appropriate; and providing such functions common to a nurse practitioner for which the ARNP is educationally and experientially prepared.
New Jersey
New Jersey Board of Nursing: In addition to all other tasks which a registered professional nurse may, by law, perform, an advanced practice nurse may manage preventive care services, and diagnose and manage deviations from wellness and long-term illnesses, consistent with the needs of the patient and within the scope of practice of the advanced practice nurse, by: (1) initiating laboratory and other diagnostic tests; (2) prescribing or ordering medications and devices, as authorized by subsections b. and c. of this section; and (3) prescribing or ordering treatments, including referrals to other licensed health care professionals, and performing specific procedures in accordance with the provisions of this subsection.
New Mexico
New Mexico Board of Nursing: Practice by CNMs encompasses independently providing a full range of primary health care services for women from adolescence to beyond menopause. These services include primary care, gynecologic and family planning services, pre-conception care, care during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period, care of the normal newborn, and treatment of male partners for sexually transmitted infections. Midwives provide initial and ongoing comprehensive assessment, diagnosis, and treatment. They conduct physical examinations; independently prescribe, distribute and administer dangerous drugs, devices and contraceptive methods, and controlled substances in Schedules II-V of the Controlled Substances Act; admit, manage and discharge patients; order and interpret laboratory and diagnostic tests; and order the use of medical devices. Midwifery care also includes health promotion, disease prevention, and individualized wellness education and counseling.
New York
New York State Office of the Professions: Licensed midwives are not supervised; they are independent practitioners. New York State law provides that licensed midwives shall have collaborative relationships with: a licensed physician who is board certified as an obstetrician-gynecologist by a national certifying body; or a licensed physician who practices obstetrics; or a hospital, that provides obstetrics through a licensed physician having obstetrical privileges at such institution, that provide for consultation, collaborative management and referral to address the health status and risks of his or her patients and that includes plans for emergency medical gynecological and/or obstetrical coverage. A midwife shall maintain documentation of such collaborative relationships and shall make this information available to his or her patients.
Visit our New York state page to learn how to be become a midwife in NY.
North Dakota
North Dakota Board of Nursing: The scope of practice for a registered nurse with advanced licensure is based upon an understanding that a broad range of health care services can be appropriately and competently provided by a registered nurse with validated knowledge, skills, and abilities in specific practice areas. The health care needs of citizens in North Dakota require that nurses in advanced practice roles provide care to the fullest extent of their scope of practice. The advanced practice registered nurse retains the responsibility and accountability for that scope of practice and is ultimately accountable to the patient within the Nurse Practices Act.
Oregon
Oregon Board of Nursing: Nurse Midwife Nurse Practitioner (NMNP) The Nurse Midwife Nurse Practitioner independently provides health care to women, focusing on pregnancy, childbirth, the postpartum period, care of the newborn, and the family planning and gynecological needs of women. The scope of practice includes treating the male partners of their female clients for sexually transmitted diseases, and reproductive health. Counseling related to sexuality, relationship, and reproductive issues are included in this scope;
Rhode Island
Rhode Island State Department of Health: The license to practice midwifery authorizes the holder to practice the independent management of cases of normal childbirth, including prenatal, intrapartum, postpartum, and normal newborn care, and well woman care including the management of common health problems that provides for consultation, collaborative management, or referral as indicated by the health status of the client in accordance with standards established by the American College of Nurse-Midwives.
Utah
Utah Department of Commerce, Division of Occupational and Professional Licensing: The practice of nurse-midwifery is defined to mean the practice of nursing within the generally recognized scope and standards of nurse midwifery as defined by rule and consistent with professionally recognized preparations and educational standards of a certified nurse midwife by a person licensed under this chapter, which practice includes:(i) having a safe mechanism for obtaining medical consultation, collaboration, and referral with one or more consulting physicians who have agreed to consult, collaborate, and receive referrals, but who are not required to sign a written document regarding the agreement.
Vermont
Vermont Board of Nursing: Graduates with fewer than 24 months and 2,400 hours of licensed active advanced nursing practice in an initial role and population focus or fewer than 12 months and 1,600 hours for any additional role and population focus shall have a formal agreement with a collaborating provider as required by board rule. APRNs shall have and maintain signed and dated copies of all required collaborative provider agreements as part of the practice guidelines. An APRN who satisfies the requirements to engage in solo practice shall notify the board that these requirements have been met.
Washington
Washington State Nursing Quality Care Assurance Commission: Advanced registered nursing practice means the performance of the acts of a registered nurse and the performance of an expanded role in providing health care services as recognized by the medical and nursing professions, the scope of which is defined by rule by the commission. Upon approval by the commission, an advanced registered nurse practitioner may prescribe legend drugs and controlled substances contained in Schedule V of the Uniform Controlled Substances Act and Schedules II through IV.
Washington, DC
District of Columbia Board of Nursing: The nurse-midwife may perform any of the following acts including:
- Manage the care of the normal obstetrical patient
- Perform minor surgical procedure;
- Manage the normal obstetrical patient during labor and delivery to include amniotomy, episiotomy, and repair;
- Initiate and perform local anesthetic procedures and order the necessary anesthetic agents to perform the procedures;
- Manage care of the newborn;
- Perform post-partum examination;
- Provide gynecological care for women;
- Prescribe appropriate medications;
- Provide family planning and STD services;
- Provide primary health care; and
A certified nurse-midwife shall have authority to prescribe legend drugs and controlled substances only while licensed.
Wyoming
Wyoming Board of Nursing: The regulations do not define nurse-midwifery but, rather, adopt the respective national organizations’ scope of practice statements for each specialty, which would include ACNM’s Standards for the Practice of Nurse-Midwifery.